The Iowa Watershed Approach (IWA) is a vision for Iowa’s future that voluntarily engages stakeholders throughout the watershed to achieve common goals, while moving toward a more resilient state.
In January 2016, the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD) announced an award of nearly $97M to the state of Iowa for its proposal titled, The Iowa Watershed Approach for Urban and Rural Resilience. The award was made under HUD’s National Disaster Resilience Competition designed to fund cutting-edge projects that address unmet needs from past disasters while addressing the vulnerabilities that could put Americans in harm’s way during future disasters.
The Iowa Watershed Approach (IWA) represents a program through which Iowans are working together to address factors that contribute to floods. This approach is consistent with other statewide programs in Iowa to reduce flooding and improve water quality, such as the Iowa Flood Mitigation Program and the Iowa Nutrient Reduction Strategy.
Nine distinct watersheds representing different Iowa landforms will serve as project sites for the IWA. Each will form a Watershed Management Authority, develop a hydrologic assessment and watershed plan, and implement projects in the upper watershed to reduce the magnitude of downstream flooding and to improve water quality during and after flood events. Flood resilience programs will be implemented in each watershed to help increase community resilience to future floods. The nine project watersheds are:
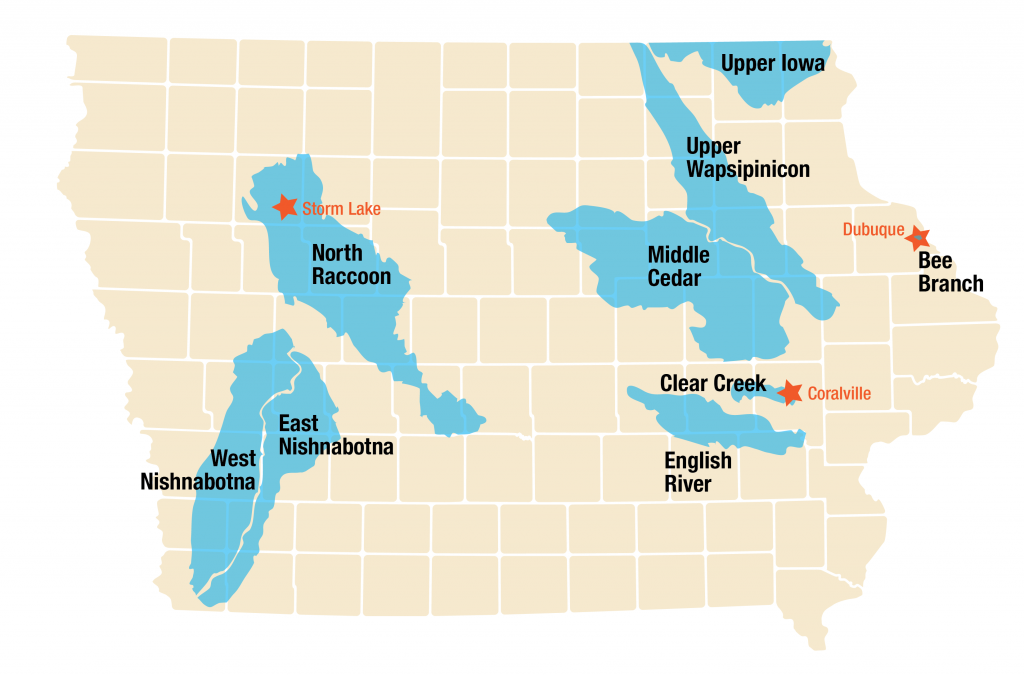
- Upper Iowa River Watershed
- Upper Wapsipinicon River Watershed
- Bee Branch Creek (Dubuque) Watershed
- Middle Cedar River Watershed
- Clear Creek Watershed
- English River Watershed
- North Raccoon River Watershed
- East Nishnabotna River Watershed
- West Nishnabotna River Watershed
- Reduce flood risk
- Improve water quality
- Increase flood resilience
- Engage stakeholders through collaboration and outreach/education
- Improve quality of life and health, especially for susceptible populations
- Develop a program that is scalable and replicable throughout the Midwest and the United States
